Luke's Car Tips & Auto Maintenance Advice
Luke's posts regular blogs to offer you great information and advice about your car maintenance. Check back often for new posts. Search for a specific topic!
 Luke Shaff
Luke Shaff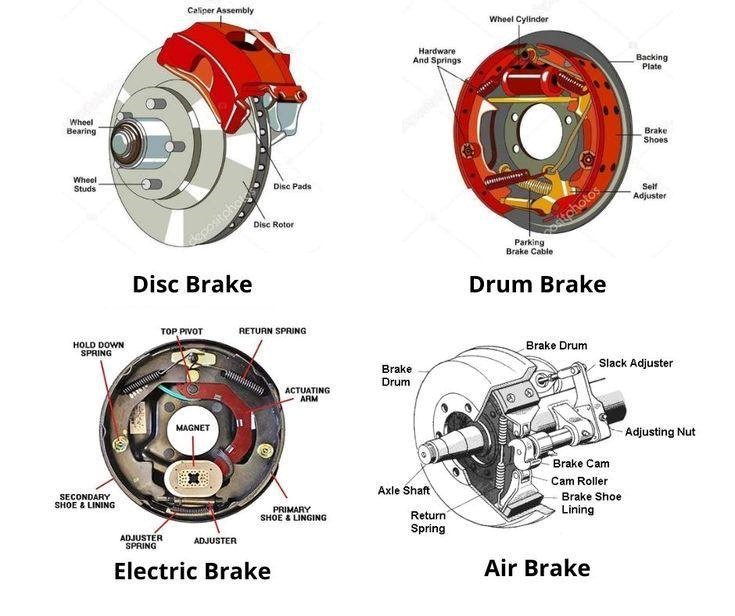
Brakes are a crucial component in any vehicle, ensuring the safety and control of the vehicle under various driving conditions. There are several types of brake systems used in vehicles today, each with its unique mechanism and applications. Let's explore the differences between the four main types of brakes: Disc Brakes, Drum Brakes, Electric Brakes, and Air Brakes.
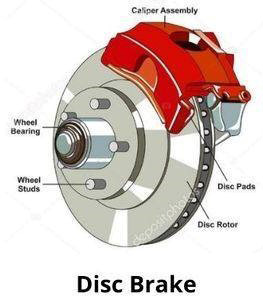 Disc Brakes
Disc Brakes
Disc brakes are commonly found on the front wheels of modern vehicles and are also used on all four wheels of many cars. The key components of a disc brake include:
When you press the brake pedal, the caliper squeezes the brake pads against the disc rotor, creating friction that slows the wheel's rotation. Disc brakes are known for their excellent stopping power and ability to dissipate heat, making them highly effective for high-speed braking.
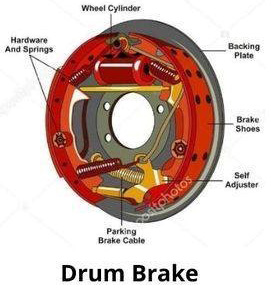 Drum Brakes
Drum Brakes
Drum brakes are often found on the rear wheels of many vehicles, especially older models. The main components of a drum brake include:
When the brake pedal is pressed, the brake shoes are forced outward against the drum's interior, creating friction that slows the wheel. Drum brakes are less effective at dissipating heat compared to disc brakes, but they are simpler and often cheaper to manufacture.
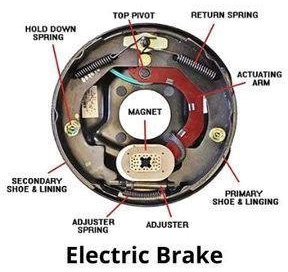 Electric Brakes
Electric Brakes
Electric brakes are commonly used in trailers and some specialized vehicles. They consist of the following key components:
When the towing vehicle's brake controller sends an electrical signal, the electromagnet is activated. This causes the actuating arm to push the brake shoes against the drum, slowing the wheel. Electric brakes allow for smooth, adjustable braking and are often used in applications where precise control is needed.
 Air Brakes
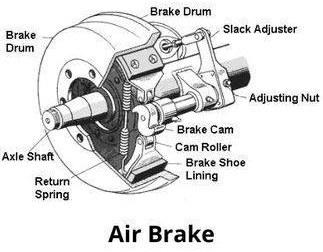
Air Brakes
Air brakes are predominantly used in heavy-duty vehicles like trucks and buses. They consist of the following primary components:
Air brakes use compressed air to apply pressure to the brake shoes. When the brake pedal is pressed, air is released from the brake chamber, pushing the brake shoes against the drum. Air brakes are highly reliable and can provide powerful braking force, making them ideal for large, heavy vehicles.
Each type of brake system has its specific advantages and applications. Disc brakes offer superior heat dissipation and stopping power, making them ideal for high-speed vehicles. Drum brakes, while not as efficient at heat dissipation, are simpler and more cost-effective for many applications. Electric brakes provide adjustable and smooth braking for trailers, while air brakes deliver the robust braking force needed for heavy-duty vehicles. Understanding the differences between these brake systems can help you appreciate the engineering behind your vehicle's braking performance and choose the right type of brakes for your needs.