Understanding the Anatomy of a Car Starter
By: Luke Shaff ~
8/15/2024
When you turn the key or press the start button in your car, a sequence of actions takes place under the hood, leading to the engine roaring to life. One crucial component in this process is the starter. Understanding the anatomy of a car starter can help you appreciate how this small but mighty device plays a pivotal role in your vehicle's operation. In this post, we'll break down the starter's anatomy in a simple and accessible way.
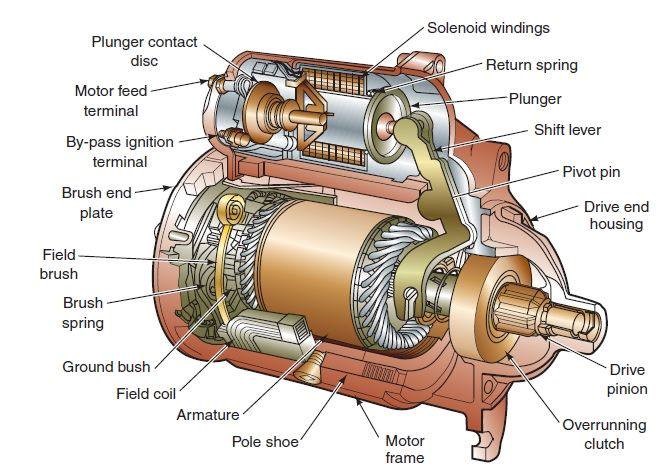
Key Components of a Car Starter
- Solenoid Windings: These are coils of wire that create a magnetic field when electric current passes through them. The magnetic field generated by the solenoid windings is crucial for the starter's operation.
- Plunger: The plunger is a movable iron core that reacts to the magnetic field created by the solenoid windings. It moves to engage the starter gear with the engine's flywheel.
- Return Spring: This spring ensures that the plunger returns to its original position after the starter has done its job. It helps in disengaging the starter gear from the flywheel.
- Shift Lever: Connected to the plunger, the shift lever helps in moving the starter gear into engagement with the flywheel.
- Pivot Pin: This pin allows the shift lever to pivot and function correctly as the plunger moves.
- Drive End Housing: This part of the starter encloses the drive mechanism and supports the other components.
- Drive Pinion: The drive pinion is a small gear that meshes with the engine's flywheel to turn the engine over.
- Overrunning Clutch: This clutch ensures that the drive pinion can turn the flywheel but prevents the flywheel from turning the pinion, protecting the starter from damage.
- Motor Frame: The motor frame houses the entire starter assembly, providing structural support.
- Armature: The armature is a rotating component inside the starter motor. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, driving the drive pinion.
- Pole Shoe: This is a part of the starter's magnetic field system, enhancing the magnetic field created by the field coils.
- Field Coil: These coils create a magnetic field that interacts with the armature, helping it to rotate.
- Ground Brush: The ground brush completes the electrical circuit within the starter, allowing current to flow.
- Field Brush: These brushes maintain electrical contact with the rotating armature.
- Brush Spring: This spring ensures that the field brushes stay in contact with the armature, maintaining a consistent electrical connection.
- Brush End Plate: This plate holds the brushes and springs in place.
- By-pass Ignition Terminal: This terminal is part of the electrical system, helping to control the flow of current to the starter.
- Motor Feed Terminal: This terminal provides power to the starter motor.
- Plunger Contact Disc: This disc helps in making and breaking the electrical connection as the plunger moves.
Each of these components works in harmony to ensure that your car starts smoothly every time you turn the key. The starter motor is a fascinating piece of engineering that exemplifies the intricate and precise nature of automotive technology.
Understanding the starter's anatomy can give you a better appreciation of how your car works and what goes into maintaining it. Regular maintenance and timely repairs can keep your starter and the entire starting system in good working condition, ensuring your vehicle remains reliable.
Feel free to reach out if you have any questions or need further clarification on any of the starter components. Happy driving!
 Luke Shaff
Luke Shaff